What Two Branches Of Government Makeup Congress
2.2 The Branches of Government
Learning Objectives
- Identify the three branches of government.
- Ascertain the head of the federal and state legislative branches of government.
- Compare the Senate and the House of Representatives.
- Ascertain the head of the federal and state executive branches of authorities.
- Ascertain the head of the federal and state judicial branches of government.
The federal Constitution was written to ensure that government power is distributed and never full-bodied in i or more than areas. This philosophy is served by federalism, where the federal government shares power with the states. It is as well further served by dividing the government into three branches, all responsible for different government duties and all checking and balancing each other. The 3 branches of government are detailed in Articles I–III of the federal Constitution and are the legislative branchThe co-operative of regime responsible for creating statutory law. , the executive branchThe branch of authorities responsible for enforcing statutory law. , and the judicial branchThe branch of government responsible for interpreting statutory and ramble police force(south). . While the federal Constitution identifies only the federal branches of government, the principle of checks and balances applies to the states as well. Almost states identify the iii state branches of government in their state constitution.
Each branch of government has a distinct authority. When one co-operative encroaches on the duties of another, this is called a violation of separation of powersEach regime co-operative must act only inside the scope prepare forth in the Constitution. . The courts make up one's mind whether a government co-operative has overstepped its boundaries because courts interpret the Constitution, which describes each branch's sphere of influence. Thus the judicial branch, which consists of all the courts, retains the residue of power.
The Legislative Branch
The legislative branch is responsible for creating statutory laws. Citizens of a land tin can vote for some state statutes past ballot, but the federal legislative co-operative enacts all federal statutes. In the federal government, the legislative branch is headed by Congress. States' legislative branches are headed by a land legislature. Congress is bicameralMade upward of two houses. , which means it is made up of two houses. This system provides equal representation among the several states and by citizens of the Us. States are represented past the SenateThe business firm of Congress responsible for representing each state. . Every state, no matter how large or small, gets two senators. Citizens are represented by the Firm of RepresentativesThe house of Congress responsible for representing each citizen of the United States. . Membership in the House of Representatives is based on population. A heavily populated land, like California, has more representatives than a sparsely populated state, like Alaska. States' legislatures are generally bicameral and have a similar structure to the federal system.
Figure ii.4 Diagram of the Legislative Co-operative
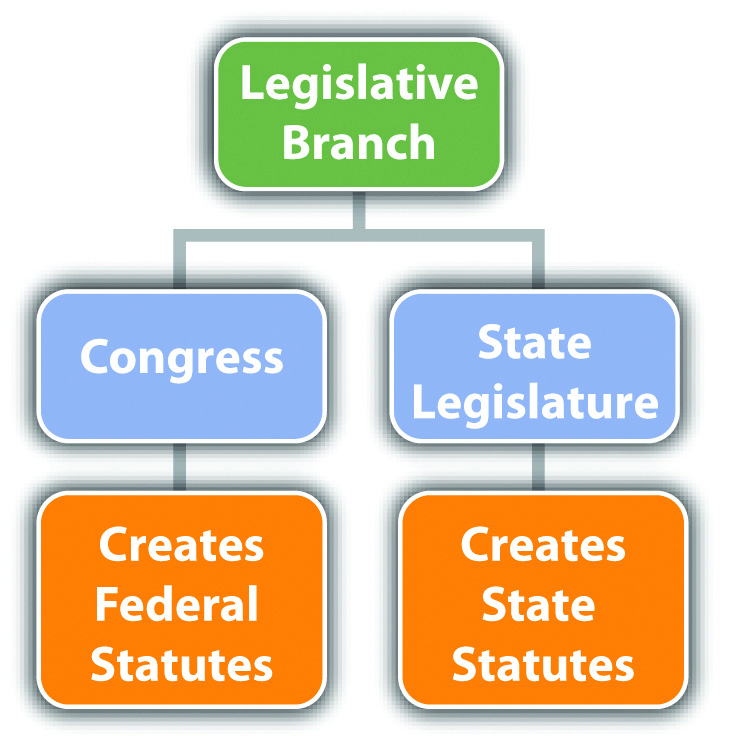
Examples of Legislative Branch Checks and Balances
The legislative branch tin check and balance both the executive branch and the judicial branch. Congress can impeach the president of the United States, which is the first step toward removal from office. Congress can also enact statutes that supercede judicial opinions, every bit discussed in Affiliate one "Introduction to Criminal Police force". Similarly, land legislature can also impeach a governor or enact a land statute that supersedes a state case constabulary.
The Executive Co-operative
The executive branch is responsible for enforcing the statutes enacted by the legislative branch. In the federal authorities, the executive branch is headed past the president of the United States. States' executive branches are headed by the governor of the state.
Figure ii.v Diagram of the Executive Branch
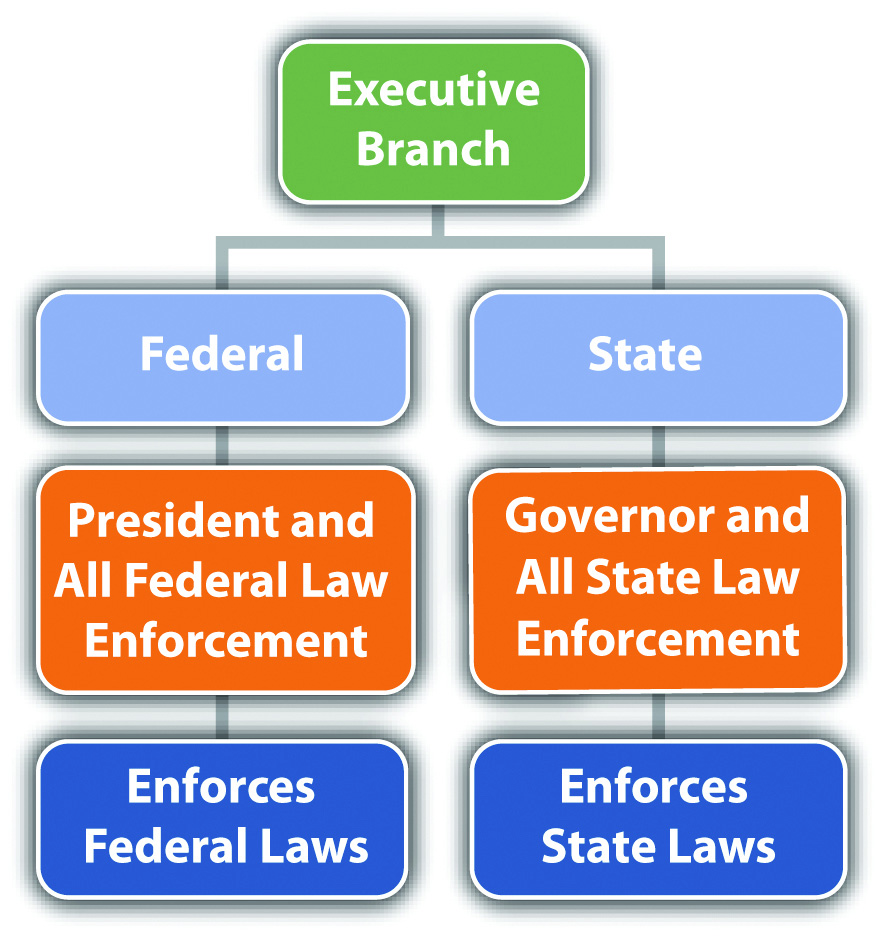
Examples of Executive Branch Checks and Balances
The executive branch can bank check and residual both the legislative co-operative and the judicial branch. The president of the The states can veto statutes proposed past Congress. The president also has the potency to nominate federal justices and judges, who thereafter serve for life. State executive branches take like cheque and balancing authority; a governor can generally veto statutes proposed by state legislature and tin can engage some state justices and judges.
The Judicial Branch
The judicial co-operative is responsible for interpreting all laws, including statutes, codes, ordinances, and the federal and state constitutions. This power is all encompassing and is the basis for judicial review, referenced in Affiliate 1 "Introduction to Criminal Law". It allows the judicial branch to invalidate any unconstitutional law in the statutory source of law and also to change the federal and state constitutions past estimation. For example, when a court creates an exception to an subpoena to the constitution, it has made an informal change without the necessity of a national or state consensus. The federal judicial branch is headed by the US Supreme Court. Each country'due south judicial co-operative is headed by the highest-level state appellate court. Members of the judicial branch include all judges and justices of every federal and state court in the court organisation, which is discussed soon.
Figure 2.6 Diagram of the Judicial Branch
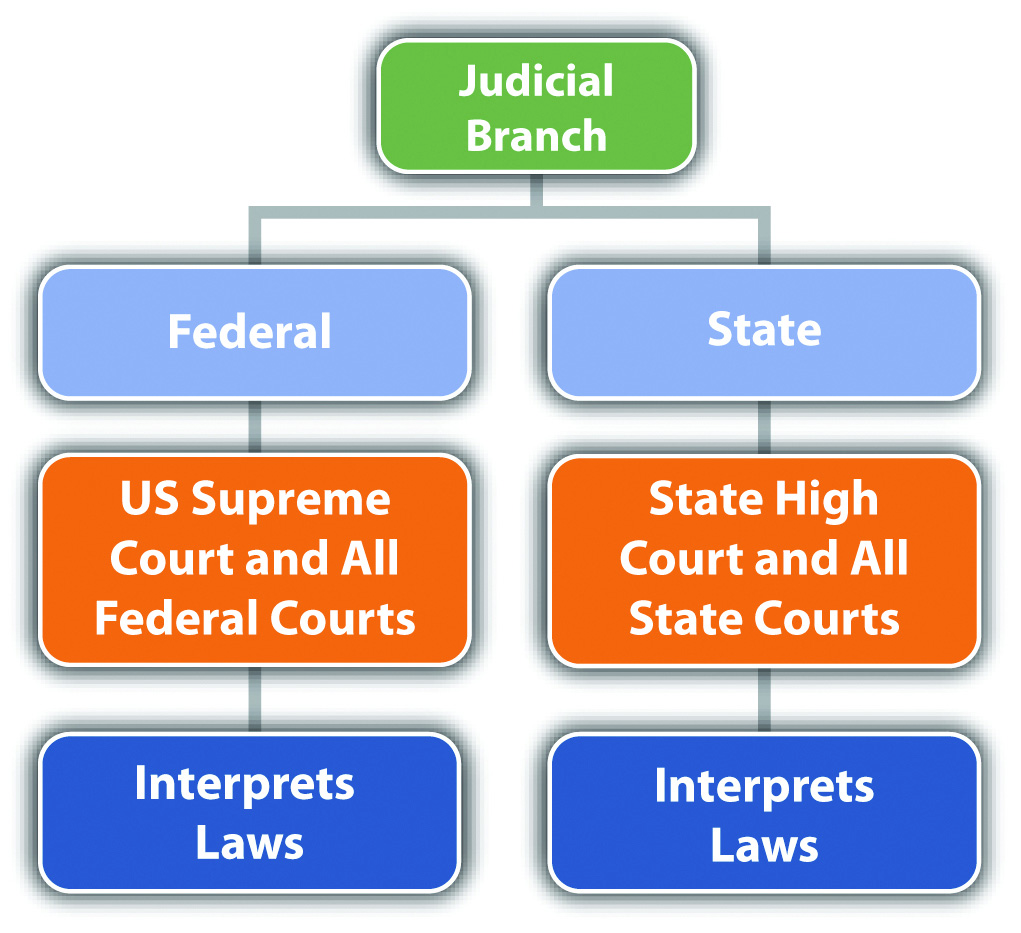
Examples of Judicial Branch Checks and Balances
The judicial branch can check and balance both the legislative branch and the executive branch. The Usa Supreme Court can invalidate statutes enacted by Congress if they disharmonize with the Constitution. The The states Supreme Court can too prevent the president from taking action if that action violates separation of powers. The land courts tin likewise nullify unconstitutional statutes passed past the land legislature and void other executive branch actions that are unconstitutional.
Tabular array 2.1 The Most Prominent Checks and Balances between the Branches
| Government Co-operative | Duty or Dominance | Check and Residual | Government Branch Checking and Balancing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legislative | Create statutes | President tin veto | Executive |
| Executive | Enforce statutes | Congress tin override presidential veto past ii/3 majority | Legislative |
| Judicial | Translate statutes and Constitution | President nominates federal judges and justices | Executive |
| Executive | Enforce statutes | Senate can confirm or reject presidential nomination of federal judges and justices | Legislative |
| Executive | Enforce statutes | Congress tin can impeach the president | Legislative |
| Legislative | Create statutes | Courts tin can invalidate unconstitutional statutes | Judicial |
| Executive | Enforce statutes | Courts tin can invalidate unconstitutional executive activity | Judicial |
| Judicial | Interpret statutes and Constitution | Statutes tin can supplant case law | Legislative |
Primal Takeaways
- The iii branches of government are the legislative branch, the executive co-operative, and the judicial co-operative.
- The head of the federal legislative branch of government is Congress. The head of the land legislative branch of regime is the country legislature.
- The Senate represents every state as because each state has two senators. The Business firm of Representatives represents each citizen equally because states are assigned representatives based on their population.
- The caput of the federal executive branch of government is the president. The head of each state executive branch of government is the governor.
- The head of the federal judicial branch of government is the US Supreme Court. The head of each country judicial branch of government is the highest-level state appellate courtroom.
Exercises
Respond the following questions. Check your answers using the answer fundamental at the terminate of the chapter.
- A mayor enacts a policy that prohibits police officers in his city from enforcing a state law prohibiting the possession and use of marijuana. The mayor's policy specifically states that within the metropolis limits, marijuana is legal to possess and use. Which ramble principle is the mayor violating? Which co-operative of government should cheque and balance the mayor's behavior in this matter?
- Read Youngstown Sail & Tube Co. v. Sawyer, 343 U.South. 579 (1952). In Youngstown, President Truman seized control of steel mills to avoid a strike, using his authority as commander in chief of the armed forces. President Truman wanted to ensure steel production during the Korean War. Did the US Supreme Courtroom uphold President Truman's action? Why or why not? The instance is bachelor at this link: http://supreme.justia.com/usa/343/579/.
- Read Hamdi 5. Rumsfeld, 542 U.South. 507 (2004). In Hamdi, the U.s.a. Supreme Courtroom reviewed the US Courtroom of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit's decision prohibiting the release of a US citizen who was held as an enemy combatant in Virginia during the Transitional islamic state of afghanistan War. The citizen's detention was based on a federal statute that deprived him of the opportunity to consult with an attorney or have a trial. Did the US Supreme Court defer to the federal statute? Why or why not? The instance is available at this link: http://scholar.google.com/scholar_case?example=6173897153146757813&hl=en&as_sdt=ii&as_vis=ane&oi=scholarr.
What Two Branches Of Government Makeup Congress,
Source: https://saylordotorg.github.io/text_criminal-law/s06-02-the-branches-of-government.html
Posted by: ingallsforbeartne.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Two Branches Of Government Makeup Congress"
Post a Comment